It is good to see a number of atists of Pakistan origin mentioned is this article.
Enjoy!
Art Consultant Arianne Levene Piper on Collecting in Emerging Art Markets
Source: Huffington Post
Natalie Hegert
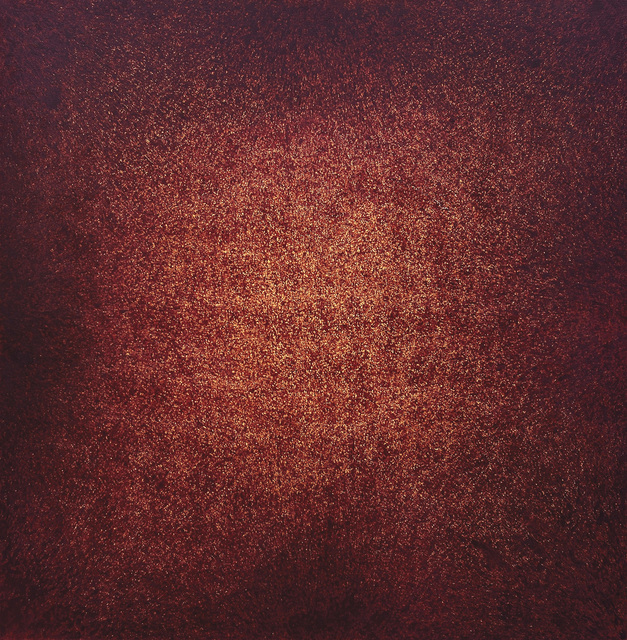
Rashid Rana, Perpetuel Paradoxe, 2010, installation view, Musee Guimet. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
In a globalized art world, a good navigator is essential. Arianne Levene Piper is a London-based art consultant and curator who advises major international collectors in Zurich, London, Stockholm, Dubai and elsewhere. With specialist knowledge on international emerging art markets including China, Japan, Korea, India, Pakistan and Iran, Levene Piper helps collectors cultivate informed outlooks and museum-quality collections of art that don't give in to trends or succumb to speculation. MutualArt talked with Levene Piper about her experiences traveling the globe in search of artists, the rise of the art consultant profession and the emergence and development of the globalized art marketplace.

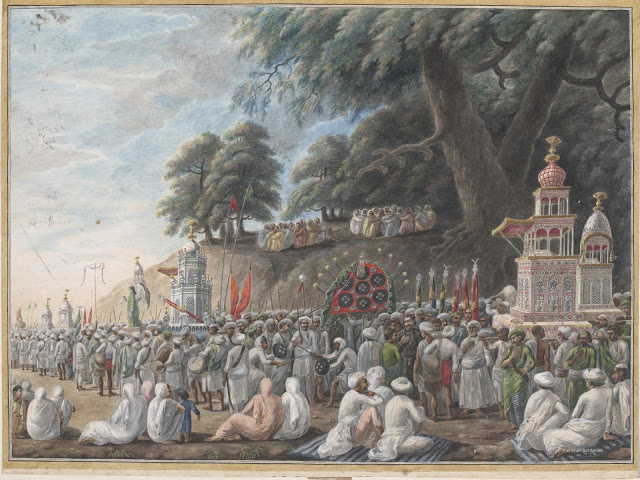
Installation view of works by Reza Aramesh, Lost in Paradise. Du spirituel dans l'art actuel, 2012, Espace Sévigné. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
Natalie Hegert: After your experience working at Sotheby's and UBS, what prompted you to strike out with your own independent art advisory firm?
Arianne Levene Piper: One of the main deciding factors was my desire to work with Chinese Contemporary Art; in 2005 there were hardly any galleries or dealers working with Chinese Contemporary Art in London, and very few -- if any -- Contemporary Asian Departments at the auction houses. It felt like a huge oversight given the ever-growing importance of China on an economic, political and cultural level -- not only in the commercial market, but also in the wider art world's consciousness. There was such an abundance of energy and creativity in China that it was baffling that this was not being reflected in Europe and the US. I felt the first obvious step in readdressing this balance was to start out on my own.

Installation view of works by Behrouz Rae and Nazgol Ansarinia, Made in Iran, 2009, Asia House, London. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: What brought you to specialize in emerging art markets, and what initially drew you to East Asia and the Middle East? How have you seen these markets develop over time?
ALP: As I mentioned, in 2004 - 2005 very few people were engaging with Contemporary Chinese art but it was a very exciting time to visit China as things were very much in flux. The emergence of the 798 District in Beijing and Moganshanlu in Shanghai were pivotal in the growth of a Contemporary art scene in the country; more and more galleries began to open there and the scene begun to flourish. In 2007 Guy and Myriam Ullens opened the Ullens Center for Contemporary Art (UCCA), presenting both international and Chinese artists from established and emerging backgrounds; the following year saw the launch of ART HK -- the Hong Kong International Art Fair. This wind-change in China, and beyond, then coincided with the seminal Saatchi show The Revolution Continues in London, which took Chinese Contemporary Art as its focus and introduced record-breaking numbers of visitors to the genre in 2008. Saatchi followed this with a show of Indian and then Middle Eastern Art, and places such as Initial Access, the home to Frank Cohen's collection, followed suit.
As prices increased I decided to then explore the emerging art worlds in India and the Middle East. Again this proved to be a dynamic time to visit these locations and I spent months travelling to these regions, meeting artists and really exploring the art being produced. Many buyers at the time noticed the trend in emerging art and wanted to snap up anything and everything that was being made -- but they weren't truly engaging with the works. This caused a speculative bubble in these markets -- aided by the fact that many financial sectors were also looking at investing in MEA and BRIC regions at the same time. The fact that I had visited these regions and engaged with the art scenes in the respective countries became key to my understanding of the work. I was able to identify who the main players really were (be they artists, collectors or galleries) and make educated and calculated decisions on what to purchase; I didn't just follow auctions from London, which can often provide a distorted view of the wider market and a piece's art historical worth.
Of course the art market is highly speculative and a lot of people who drive booms in emerging markets are in the trade; buying at the right time is always crucial.
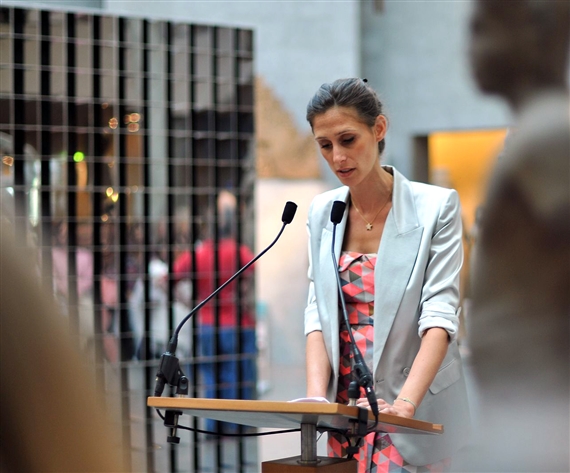
Arianne Levene Piper speaking at Rashid Rana, Perpetuel Paradoxe, 2010, Musée Guimet. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: It must be quite exciting to travel around, discovering new artists and becoming acquainted with art scenes across the globe. Are there any particular incidents or anecdotes that stand out for you from your travels?
ALP: Going for dinner with artists in China always entailed discovering new and unusual foods, even if this sometimes meant I wasn't quite sure what it was I was eating. Once I mistook a plate of miniature dried prawns for rice, which was quite a surprise!
I also remember one instance when my brother, who traveled around India on a research trip with me back in 2008, politely accepted some homemade liqueur at an Indian artist's home. Although it was delicious we spent the next three days bound to our hotel room with doctors on call...
Finally, getting in and out of Iran was often dicey and quite nerve wracking; it sometimes felt a bit like the final scene from Argo. However, I knew these opportunities could not be passed by and in some ways this only propelled my drive to meet new artists and to visit different places.

Installation view of works by Shezad Dawood, Lost in Paradise. Du spirituel dans l'art actuel, 2012, Espace Sévigné. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: You've also curated a number of exhibitions, including Lost in Paradise: Du spiritual dans l'art actual at Loft Sévigné in Paris, an exhibition of Pakistani artist Rashid Rana at the Musée Guimet in Paris and Made In Iran at Asia House in London. How does curating compare to consulting? I imagine these activities feed into each other quite a lot.
ALP: A major difference between curating and advising is that with curation you work primarily with the artists; this of course is a very different experience to dealing with clients. I have certainly found the creative side of curating extremely rewarding, and through this practice I've found another way in which to explore emerging genres and introduce lesser-known artists to international audiences. However, ultimately I feel that building collections is my passion; my expertise lends itself particularly to the advisory role.

Installation view of work by Idris Khan, Lost in Paradise. Du spirituel dans l'art actuel, 2012, Espace Sévigné. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: There's been a noted rise in the number of art advisers in the recent past, and now even some online ventures that purport to help would-be collectors navigate the art world and facilitate connections. Do you think it's necessary for a new collector to become introduced to the art world via a third party in some capacity (even if that third party is a friend, not a professional)? What is it about the art world that is so opaque and intimidating that the intermediary profession is growing at such a rate? Or is there something else that is contributing to this trend?
ALP: I think people often do find the art world intimidating and advisors can be a way into what feels like quite a clandestine world. However my work isn't solely about providing access, it is also about working with individuals -- whether they are completely new to the art world as you mention, or already well informed -- to cultivate or refine their own knowledge of the art landscape. I work to develop each client's individual, distinctive appreciation of art and I educate and support them on the creation of considered and dynamic collections; for me this is much more rewarding for an advisor than simply facilitating a collection's growth.

Shinro Ohtake, Red Head, 1995, dye, dust on paper, 99.8 x 70.3 cm. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: You have your own personal collection of art, too. Can you tell us a bit about your own collection and any favorite works?
ALP: I really only ever buy what I love. Like many people in London I sadly don't have a huge amount of space, so it makes sense that most of the things that I buy are small in scale. Some of my favorite works in my collection include a lovely painting by the Japanese artist Shinro Ohtake who works with found images from urban culture and the media, and turns them into beautiful works of art. I am also very proud of my latest purchase, a Yoshitomo Nara drawing.

Yoshitomo Nara, On your Way?, 2015, colored pencil on envelope, 24 x 33 cm. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: Besides the maxim to "buy only what you love," what other piece of advice do you think collectors should follow?
ALP: I cannot disconnect art from life; art makes me feel very alive. Indeed, I can't imagine my life without it. Auguste Rodin once said about art: "The main thing is to be moved, to love, to hope, to tremble, to live."
However with regards to collecting art here are three maxims from very different people that come to mind:
"Collectors are happy people." - Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
"Buying art is the same thing as falling in love." - Nohra Haime
"The art one chooses to collect becomes a self-portrait." - Dennis Heckler
I think that covers most bases!
--Natalie Hegert
In a globalized art world, a good navigator is essential. Arianne Levene Piper is a London-based art consultant and curator who advises major international collectors in Zurich, London, Stockholm, Dubai and elsewhere. With specialist knowledge on international emerging art markets including China, Japan, Korea, India, Pakistan and Iran, Levene Piper helps collectors cultivate informed outlooks and museum-quality collections of art that don't give in to trends or succumb to speculation. MutualArt talked with Levene Piper about her experiences traveling the globe in search of artists, the rise of the art consultant profession and the emergence and development of the globalized art marketplace.

Installation view of works by Reza Aramesh, Lost in Paradise. Du spirituel dans l'art actuel, 2012, Espace Sévigné. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
Natalie Hegert: After your experience working at Sotheby's and UBS, what prompted you to strike out with your own independent art advisory firm?
Arianne Levene Piper: One of the main deciding factors was my desire to work with Chinese Contemporary Art; in 2005 there were hardly any galleries or dealers working with Chinese Contemporary Art in London, and very few -- if any -- Contemporary Asian Departments at the auction houses. It felt like a huge oversight given the ever-growing importance of China on an economic, political and cultural level -- not only in the commercial market, but also in the wider art world's consciousness. There was such an abundance of energy and creativity in China that it was baffling that this was not being reflected in Europe and the US. I felt the first obvious step in readdressing this balance was to start out on my own.

Installation view of works by Behrouz Rae and Nazgol Ansarinia, Made in Iran, 2009, Asia House, London. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: What brought you to specialize in emerging art markets, and what initially drew you to East Asia and the Middle East? How have you seen these markets develop over time?
ALP: As I mentioned, in 2004 - 2005 very few people were engaging with Contemporary Chinese art but it was a very exciting time to visit China as things were very much in flux. The emergence of the 798 District in Beijing and Moganshanlu in Shanghai were pivotal in the growth of a Contemporary art scene in the country; more and more galleries began to open there and the scene begun to flourish. In 2007 Guy and Myriam Ullens opened the Ullens Center for Contemporary Art (UCCA), presenting both international and Chinese artists from established and emerging backgrounds; the following year saw the launch of ART HK -- the Hong Kong International Art Fair. This wind-change in China, and beyond, then coincided with the seminal Saatchi show The Revolution Continues in London, which took Chinese Contemporary Art as its focus and introduced record-breaking numbers of visitors to the genre in 2008. Saatchi followed this with a show of Indian and then Middle Eastern Art, and places such as Initial Access, the home to Frank Cohen's collection, followed suit.
As prices increased I decided to then explore the emerging art worlds in India and the Middle East. Again this proved to be a dynamic time to visit these locations and I spent months travelling to these regions, meeting artists and really exploring the art being produced. Many buyers at the time noticed the trend in emerging art and wanted to snap up anything and everything that was being made -- but they weren't truly engaging with the works. This caused a speculative bubble in these markets -- aided by the fact that many financial sectors were also looking at investing in MEA and BRIC regions at the same time. The fact that I had visited these regions and engaged with the art scenes in the respective countries became key to my understanding of the work. I was able to identify who the main players really were (be they artists, collectors or galleries) and make educated and calculated decisions on what to purchase; I didn't just follow auctions from London, which can often provide a distorted view of the wider market and a piece's art historical worth.
Of course the art market is highly speculative and a lot of people who drive booms in emerging markets are in the trade; buying at the right time is always crucial.
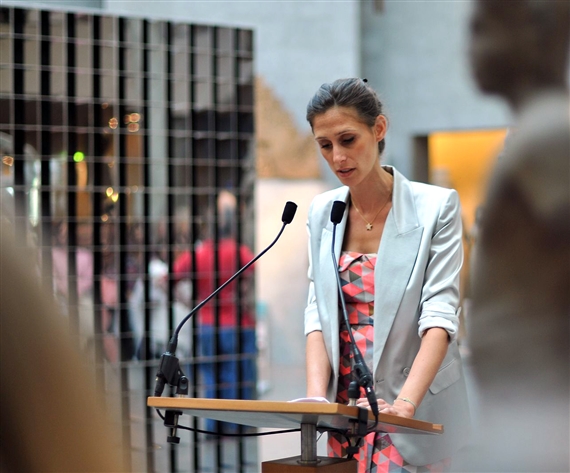
Arianne Levene Piper speaking at Rashid Rana, Perpetuel Paradoxe, 2010, Musée Guimet. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: It must be quite exciting to travel around, discovering new artists and becoming acquainted with art scenes across the globe. Are there any particular incidents or anecdotes that stand out for you from your travels?
ALP: Going for dinner with artists in China always entailed discovering new and unusual foods, even if this sometimes meant I wasn't quite sure what it was I was eating. Once I mistook a plate of miniature dried prawns for rice, which was quite a surprise!
I also remember one instance when my brother, who traveled around India on a research trip with me back in 2008, politely accepted some homemade liqueur at an Indian artist's home. Although it was delicious we spent the next three days bound to our hotel room with doctors on call...
Finally, getting in and out of Iran was often dicey and quite nerve wracking; it sometimes felt a bit like the final scene from Argo. However, I knew these opportunities could not be passed by and in some ways this only propelled my drive to meet new artists and to visit different places.

Installation view of works by Shezad Dawood, Lost in Paradise. Du spirituel dans l'art actuel, 2012, Espace Sévigné. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: You've also curated a number of exhibitions, including Lost in Paradise: Du spiritual dans l'art actual at Loft Sévigné in Paris, an exhibition of Pakistani artist Rashid Rana at the Musée Guimet in Paris and Made In Iran at Asia House in London. How does curating compare to consulting? I imagine these activities feed into each other quite a lot.
ALP: A major difference between curating and advising is that with curation you work primarily with the artists; this of course is a very different experience to dealing with clients. I have certainly found the creative side of curating extremely rewarding, and through this practice I've found another way in which to explore emerging genres and introduce lesser-known artists to international audiences. However, ultimately I feel that building collections is my passion; my expertise lends itself particularly to the advisory role.

Installation view of work by Idris Khan, Lost in Paradise. Du spirituel dans l'art actuel, 2012, Espace Sévigné. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: There's been a noted rise in the number of art advisers in the recent past, and now even some online ventures that purport to help would-be collectors navigate the art world and facilitate connections. Do you think it's necessary for a new collector to become introduced to the art world via a third party in some capacity (even if that third party is a friend, not a professional)? What is it about the art world that is so opaque and intimidating that the intermediary profession is growing at such a rate? Or is there something else that is contributing to this trend?
ALP: I think people often do find the art world intimidating and advisors can be a way into what feels like quite a clandestine world. However my work isn't solely about providing access, it is also about working with individuals -- whether they are completely new to the art world as you mention, or already well informed -- to cultivate or refine their own knowledge of the art landscape. I work to develop each client's individual, distinctive appreciation of art and I educate and support them on the creation of considered and dynamic collections; for me this is much more rewarding for an advisor than simply facilitating a collection's growth.

Shinro Ohtake, Red Head, 1995, dye, dust on paper, 99.8 x 70.3 cm. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: You have your own personal collection of art, too. Can you tell us a bit about your own collection and any favorite works?
ALP: I really only ever buy what I love. Like many people in London I sadly don't have a huge amount of space, so it makes sense that most of the things that I buy are small in scale. Some of my favorite works in my collection include a lovely painting by the Japanese artist Shinro Ohtake who works with found images from urban culture and the media, and turns them into beautiful works of art. I am also very proud of my latest purchase, a Yoshitomo Nara drawing.

Yoshitomo Nara, On your Way?, 2015, colored pencil on envelope, 24 x 33 cm. Courtesy of Arianne Levene Piper.
NH: Besides the maxim to "buy only what you love," what other piece of advice do you think collectors should follow?
ALP: I cannot disconnect art from life; art makes me feel very alive. Indeed, I can't imagine my life without it. Auguste Rodin once said about art: "The main thing is to be moved, to love, to hope, to tremble, to live."
However with regards to collecting art here are three maxims from very different people that come to mind:
"Collectors are happy people." - Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
"Buying art is the same thing as falling in love." - Nohra Haime
"The art one chooses to collect becomes a self-portrait." - Dennis Heckler
I think that covers most bases!
--Natalie Hegert



























